Epsom Salt vs Himalayan Salt: Which is Better for Industry Use?
- Zayan Rauf

Key takeaways
- Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate) and Himalayan salt (sodium chloride) serve very different industrial purposes.
- Epsom salt is ideal for chemical, agricultural, and textile industries due to its magnesium and sulfate content.
- Himalayan salt is better suited for food processing, water softening, and wellness industries.
- Both salts differ in composition, solubility, and cost, so choosing the right one depends on your specific industrial application.
- Sobaan Salts ensures consistent quality, purity, and reliable sourcing for diverse industrial requirements.
In industrial settings, the choice of salt is more than just “pink or white.” Different salts serve very different chemical and functional roles. In this article, we compare Epsom Salt vs Himalayan Salt specifically for industrial use, their composition, properties, applications, and limitations so that manufacturers, importers, and industrial buyers can make informed decisions.
What Is Epsom Salt?
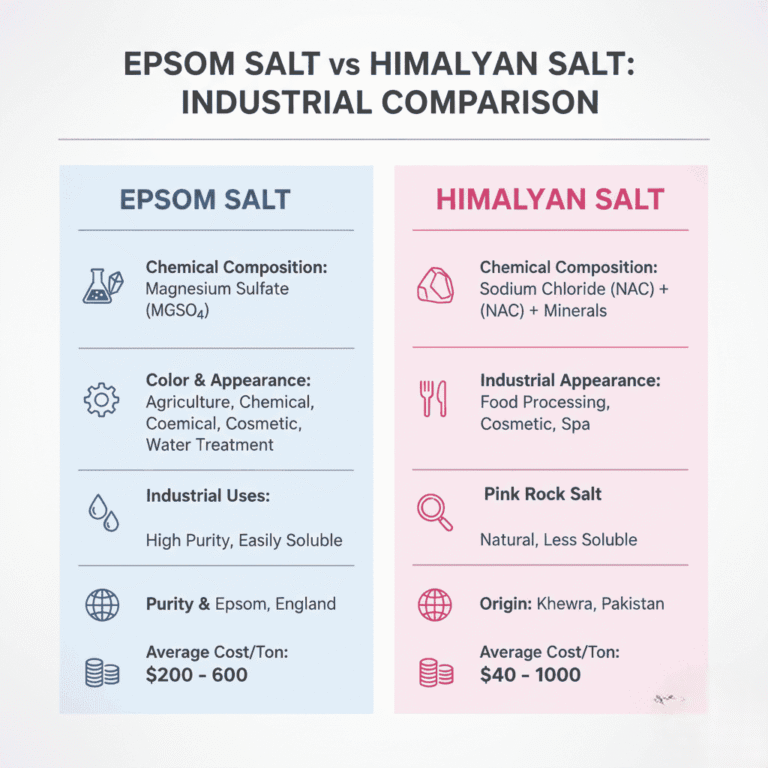
- Chemical Identity: Epsom salt is magnesium sulfate, most commonly as the heptahydrate form (MgSO₄·7H₂O). [1]
- Origin & Production: It can be produced by reacting magnesium oxide or magnesium carbonate with sulfuric acid, or extracted from natural sources.
- Properties: Highly soluble in water, neutral to mildly acidic in solution. It provides both magnesium (Mg²⁺) and sulfate (SO₄²⁻) ions.
- Purity & Grades: Industrial, agricultural, and pharmaceutical grades exist; industrial use demands very low impurities (like heavy metals, chlorides). [2]
Epsom salt is a chemical functional compound, not a “salt” in the sense of sodium chloride, which makes it valuable where magnesium or sulfate functions are needed.
Did You Know?
The name “Epsom salt” comes from a bitter saline spring in Epsom, Surrey, England, where magnesium sulfate was first isolated in natural spring waters. [3]
What Is Himalayan Salt?
- Chemical Composition: Himalayan salt is primarily sodium chloride (NaCl), with trace minerals such as potassium, calcium, and iron (which gives the pink hue). [4]
- Geological Source: It is mined from ancient evaporite beds especially from the Khewra Salt Mine in Pakistan. [5]
- Properties: Crystalline rock salt, moderate solubility in water, contains trace minerals which may require purification for some industrial uses. [6]
- Export & Market Role: Pakistan is a major exporter of Himalayan salt. In 2023, Pakistan’s salt export (including rock salt) stood at around US $75.5 million. [7]
Because Himalayan salt is essentially a variant of rock salt (halite) with minor impurities, it is used where sodium chloride is functionally needed.
Read More: Understanding the Mineral Composition of Himalayan Pink Salt
Key Differences: Epsom Salt vs Himalayan Salt
Feature | Epsom Salt | Himalayan Salt |
Main Function | Provides Mg²⁺ and SO₄²⁻ ions | Provides Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions |
Chemical Type | Magnesium sulfate compound | Sodium chloride (rock salt) |
Use Cases | Where magnesium or sulfate plays active role | Where sodium chloride is required |
Purity Concern | Must be very pure (low metals, chlorides) | Trace minerals may require refining |
Cost & Transport | Higher due to chemical processing | Lower per ton, but mining + logistic costs |
Industrial Flexibility | More specialized in chemicals | More generic but broad utility |
So the key point: they are not substitutes, except in some incidental overlap (e.g. as salts in processing). The best choice depends entirely on your industry’s chemical needs.
Industrial Applications of Epsom Salt
Because Epsom salt provides magnesium and sulfate, it finds uses in:
- Chemical & Reagent Use
It is a raw ingredient or intermediate in producing magnesium compounds, or controlling sulfate levels in reactions. [8]
- Textile Industry
In dyeing and finishing, magnesium sulfate is used as a dye fixative or weighting agent to help dyes adhere and control fabric behavior.
- Paper & Pulp Industry
It is used as a filler or in bleaching / processing to improve brightness and smoothness.
- Agriculture / Fertilizers
As a magnesium and sulfur source for soils. Especially where magnesium deficiency is known.
- Detergents & Cleaning Agents
Magnesium sulfate is used in detergent formulations to adjust viscosity, stability, or ion balance. [9]
- Water Treatment & Dehydration
It can act as a dehydrator or in certain water-processing contexts, absorbing moisture in solutions.
Because Epsom salt is a functional chemical, its value in industry depends on how well it meets purity, solubility, and reaction criteria.
Read More: Dead Sea Salt Vs Epsom Salt
Industrial Applications of Himalayan Salt
Himalayan salt, being a form of sodium chloride, is more “basic salt” and finds use in:
- Food Processing & Brining
Where NaCl is required for preservation, curing, or salt baths (though purity and food-grade standards apply).
- Water Softening / Chloride Source
In systems where sodium chloride is needed to regenerate ion-exchange resins or serve as a chloride source.
- De-icing / Melting Salt
In industrial melting or de-icing use, though its trace mineral content may limit usefulness for strict chemical uses.
- Salt Blocks & Decorative / Spa Uses
Salt blocks, halotherapy chambers, salt lamps etc. where mineral color is valued (though less relevant in heavy industry).
- Basic Salt Feed in Some Processes
Sometimes used where a chloride ion is needed and trace minerals are tolerable or removable.
Thus, Himalayan salt is useful where sodium chloride is inherently needed, not when magnesium or sulfate is desired.
Did You Know?
According to a study on Pakistan’s salt deposits, Khewra’s annual production of rock salt is ~ 350,000 tonnes of ~99% pure halite, with estimated reserves ranging from 82 million to 600 million tonnes. [10]
Which Is Better by Industry Use Case?
1. Chemical / Specialty Manufacturing
If your process requires magnesium or sulfate ions (e.g. magnesium salts, sulfate reactions, catalysts), Epsom salt is virtually irreplaceable. Himalayan salt cannot supply these ions.
2. Food / Brining / Curing
When you need clean NaCl without unwanted magnesium or sulfate, Himalayan salt (properly refined) is more appropriate.
3. Textile / Dye Processing
Epsom salt is typically preferred because magnesium sulfate helps with dye fixation; Himalayan salt (NaCl) may have some role in general salt baths, but does not replace the chemical function.
4. Water Treatment / Ion Exchange
Himalayan salt may serve as a sodium chloride source (e.g. for brine regeneration); Epsom salt won’t fulfill that role.
5. Cost / Availability Considerations
Himalayan salt is often less expensive per ton (as rock salt), easier to transport and store. Epsom salt’s value comes from its functionality, but its processing and purity requirements make it costlier.
So “better” depends on the function you need. In many industrial settings, they complement rather than compete.
Key Considerations & Limitations
- Purity & Impurities: Industrial Epsom salt must be virtually free of heavy metals or chloride; Himalayan salt often requires further purification to remove trace metals.
- Certification & Standards: Food grade, pharma grade, or technical grade certifications may be required.
- Supply & Consistency: Himalayan salt supply is tied to mining output (like from Khewra).
- Cost vs Functionality: Buying cheap salt that doesn’t perform can damage processes; better to pay for the right specification.
- Logistics & Handling: Some salts are more hygroscopic or sensitive to moisture; storage and handling matter.
- Regulations & Environmental: Some regions have limits on heavy metals or soluble salts discharge; trace minerals matter.
Conclusion & Recommendation
When comparing Epsom salt vs Himalayan salt for industrial use: there is no “one is better for all” answer. The ideal choice depends on your industry, chemical requirements, purity thresholds, and cost constraints.
- Use Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate) when your process demands magnesium, sulfate, or the special chemical behavior it enables.
- Use Himalayan salt (sodium chloride) when you simply need NaCl salts, especially in food, brining, or general salt baths.
For industrial buyers and businesses working with Sobaan Salts, I recommend that you query specifications and performance requirements first, then choose the salt accordingly. We can provide rock salt (Himalayan) with high purity, and we can also help source functional salts (like magnesium sulfate) via trusted chemical suppliers.
References:
- Fortune Business Insights. (2024). Epsom salt market size, share & COVID-19 impact analysis. Fortune Business Insights.
https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/epsom-salt-market-110266
- Maximize Market Research. (2024). Global pink Himalayan salt market: Industry analysis and forecast (2024-2030). Maximize Market Research Pvt Ltd.
https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-pink-himalayan-salt-market/109972/
- Koley, M., & Nag, S. (2019). Therapeutic and nutraceutical potential of bioactive compounds from different types of salt: A comprehensive review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 93, 1-12.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168583X19304999
- Sharma, A., & Patel, V. K. (2023). A comparative study on the mineral content and potential health benefits of Epsom salt and Himalayan pink salt. International Journal of Health Sciences and Research, 13(9), 45-55.
https://www.ijhsr.org/IJHSR_Vol.13_Issue.9_Sep2023/IJHSR21.pdf
- Procurement Resource. (2024). Epsom salt manufacturing plant project report: Manufacturing process, raw materials requirements and costs. Procurement Resource.
https://www.procurementresource.com/reports/epsom-salt-manufacturing-plant-project-report
Share This Post
Article By

