Salt Export Documentation & Compliance: A Practical Guide for Importers
- Zayan Rauf

Key takeaways
- Certificate of Origin is essential for determining tariffs and preferential trade agreements
- Bill of Lading serves three critical functions: receipt, contract, and document of title
- Commercial Invoice is required for all international commodity shipments to assess duties
- FDA Prior Notice must be submitted 2-8 hours before USA shipment arrival
- Electronic documentation (eCO, eBL) streamlines processing and reduces administrative costs
- Health certificates and quality certificates vary by destination country requirements
- Documentation errors cause 15-20% of customs delays in international food trade
International salt trade requires precise documentation and regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions. For B2B importers and exporters, understanding the complete documentation requirements prevents costly customs delays, ensures legal compliance, and maintains smooth supply chain operations. This practical guide covers essential export documents, compliance requirements, and best practices for successful Himalayan salt trade.
Proper documentation not only facilitates customs clearance but also protects the legal and financial interests of all parties involved in international salt transactions. From Certificate of Origin to Bills of Lading, each document serves a specific legal and commercial purpose in global trade operations.
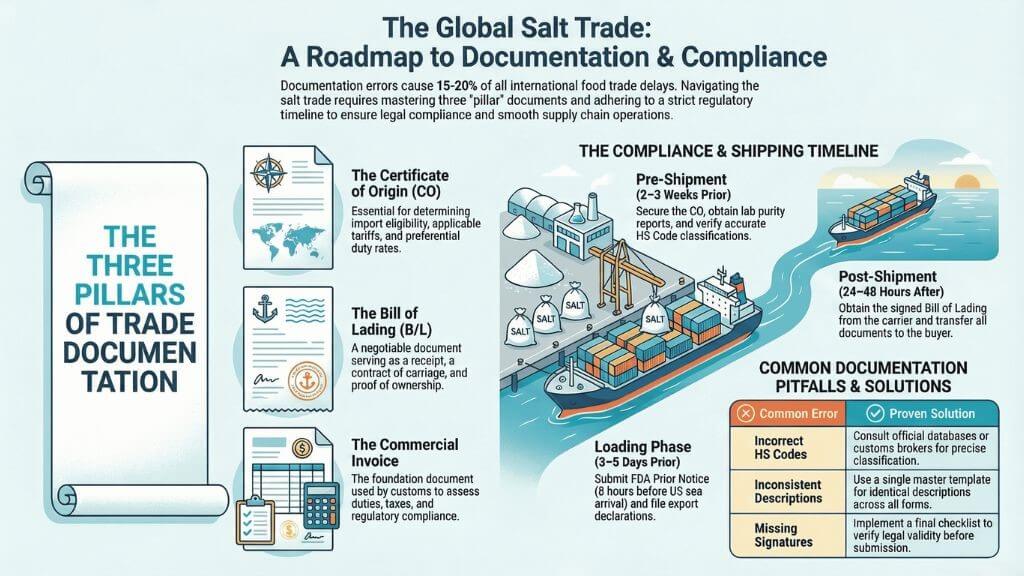
Essential Export Documents for International Salt Trade
Certificate of Origin (CO)
The Certificate of Origin proves the country where salt products originate and serves as a declaration by the exporter. This document plays a vital role in international trade by providing customs officials with necessary information to assess import eligibility and applicable duties.
Why Certificate of Origin Matters:
The ICC World Chambers Federation maintains universal guidelines for issuing Certificates of Origin, establishing global standards that millions of shipments follow annually [1]. For Himalayan pink salt exports from Pakistan, the Certificate of Origin specifically identifies the product’s source from authenticated mines in the Salt Range.
Did You Know?
Nearly every country considers the origin of imported goods when determining applicable duties. Some countries may restrict or prohibit imports from specific origins, making the Certificate of Origin a crucial document for market access [2]. Pakistani Himalayan salt benefits from geographic indication protections that require proper CO documentation.
Two Types of Certificates
- Non-Preferential Certificates: Used for goods shipped to countries without free trade agreements. These certify country of origin for general importation purposes and help customs authorities apply standard tariff rates.
- Preferential Certificates: Related to exports under Free Trade Agreements between countries offering special reduced or zero duty rates on trade. Many FTA partners accept declarative statements containing specific data elements rather than requiring specific forms.
Required Certificate Elements
Mandatory Information | Purpose |
Exporter name and address | Identifies responsible party |
Consignee details | Confirms destination buyer |
Product description | Specifies goods being shipped |
HS Code classification | Enables accurate duty assessment |
Country of origin declaration | Proves manufacturing location |
Quantity and weight | Verifies shipment details |
Signature and date | Validates authenticity |
For Himalayan pink salt suppliers in Pakistan, obtaining Chamber of Commerce certification ensures CO compliance with international standards. This certification demonstrates commitment to transparent issuance procedures and builds trust with international buyers.
Bill of Lading (B/L)
The Bill of Lading stands as one of three crucial documents in international trade, alongside insurance policies and invoices. Unlike policies and invoices which are assignable, Bills of Lading are negotiable documents that can be bought, sold, or traded while goods are in transit [3].
Three Essential Functions
- Receipt of Goods: The B/L serves as conclusive acknowledgment that goods have been loaded aboard the vessel. It documents the condition of cargo at the time of shipment, providing critical evidence for insurance claims if damage occurs during transit.
- Contract of Carriage: The B/L contains or evidences the terms of the contract between the cargo owner and carrier. This legally binding contract establishes the carrier’s obligations and liabilities for safe transport to the destination port.
- Document of Title: The B/L serves as proof of ownership for goods. In international trade where goods may change hands multiple times during transit, the B/L ensures the rightful owner can claim possession upon arrival at destination.
Bill of Lading Types
- Negotiable (Order) Bill of Lading: Allows ownership transfer multiple times during transit, offering high flexibility for traders. This type suits international salt trade where ownership may change before cargo reaches final destination.
- Straight (Non-Negotiable) Bill of Lading: Names a specific consignee and does not transfer ownership rights. Used for shipments with predetermined buyers and no intended resale during transit.
- Electronic Bill of Lading (eBL): Digital bills of lading are functionally equivalent to paper documents. Singapore, Bahrain, Germany, and the United Kingdom have enacted laws allowing eBL usage for international trade transactions.
Exporters handling bulk Himalayan salt procurement operations must ensure B/L accuracy, as federal laws govern B/L requirements and establish legal liability frameworks for carriers.
Commercial Invoice
The commercial invoice serves as the foundation for all international shipping documents and must accompany every cross-border commodity shipment. Customs officials use this document to process shipments, assess import duties and taxes, and verify regulatory compliance [4].
Mandatory Commercial Invoice Elements
Basic Identification:
- Document clearly marked as “Commercial Invoice”
- Invoice number and date of issue
- Seller (exporter) complete name and address
- Buyer (importer) complete name and address
- Consignee details if different from buyer
Product Information:
- Detailed description of salt products
- Harmonized System (HS) Code classification
- Quantity in appropriate units of measure
- Unit price and total value in agreed currency
- Country of manufacture or origin
- Terms of sale (Incoterms – FOB, CIF, etc.)
Payment Details:
- Payment terms and conditions
- Currency of transaction
- Any advance payments or deposits
- Final payment due date
The U.S. Customs and Border Protection requires commercial invoices to include the appropriate eight-digit subheading from the Harmonized Tariff Schedule. If importers are uncertain about the correct classification, customs authorities will provide assistance upon request.
Did You Know?
The commercial invoice provides customs officials with essential information to quickly determine tariffs, duties, and taxes applicable to specific products. In busy customs offices processing thousands of daily parcels, accurate commercial invoices expedite clearance and prevent costly delays [5].
For salt exports to the USA, commercial invoices must comply with FDA requirements including Prior Notice confirmation numbers and FDA facility registration details.
Regulatory and Compliance Documents
Health and Safety Certificates
Health certificates demonstrate that salt products meet food safety standards and are fit for human consumption in destination markets. Requirements vary significantly by country and product type.
Common Certification Requirements:
USA Market:
- FDA facility registration documentation
- Prior Notice Confirmation (PNC) Number
- Food safety testing certificates
- GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) status verification
European Union:
- Health certificate from competent authority
- EU Declaration of Compliance for packaging materials
- TRACES system documentation for food imports
- Compliance with EC Regulation 178/2002 food law
Middle East Markets:
- Halal certification from recognized authority
- Health certificate authenticated by embassy
- Arabic language translations of documentation
- Country-specific import permits
Asia-Pacific:
- Phytosanitary certificates when required
- Quality inspection reports from accredited labs
- Local health authority approvals
- Certificate of Free Sale (CFS) for some countries
Salt exporters offering private labeling services must coordinate documentation requirements with destination markets to ensure compliance across diverse regulatory frameworks.
Quality Certificates and Test Reports
Quality certificates provide objective evidence that salt products meet specified standards for purity, mineral composition, and safety. These documents build buyer confidence and satisfy regulatory requirements.
Essential Quality Documentation:
Laboratory Test Certificates:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) percentage analysis
- Heavy metal content testing (lead, arsenic, mercury)
- Microbiological safety testing
- Moisture content measurement
- Particle size distribution for specified grades
Quality Management Certificates:
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems)
- ISO 22000 (Food Safety Management)
- HACCP certification
- BRC Global Standard for Food Safety
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) compliance
Buyers focused on sourcing Himalayan pink salt in bulk often require these certificates before finalizing purchase agreements, making quality documentation a competitive advantage for suppliers.
Packing List
The packing list provides detailed information about the physical shipment, complementing the commercial invoice with logistics-focused data. While similar in some content, packing lists and commercial invoices serve distinct purposes.
Packing List Essential Information:
Category | Required Details |
Package Identification | Number of packages, container numbers |
Physical Specifications | Gross weight, net weight, dimensions |
Package Contents | Detailed item-by-item breakdown |
Marking Information | Package markings, case numbers |
Loading Details | Pallet configuration, container loading |
The packing list helps customs officials, freight forwarders, and warehouse personnel verify that all merchandise shipped by the exporter arrives in good order and matches documentation. It proves essential for stock-keeping, inventory management, and resolving any disputes about shipment contents [6].
Documentation Timeline and Preparation
Pre-Shipment Phase (2-3 Weeks Before)
- Obtain Certificate of Origin from Chamber of Commerce
- Secure quality certificates and lab test reports
- Prepare commercial invoice with accurate HS codes
- Verify packaging requirements for international export
Production Phase (1 Week Before)
- Conduct final product testing
- Complete packing list with weights and measures
- Arrange health certificates for destination markets
- Coordinate with freight forwarder
Loading Phase (3-5 Days Before)
- Submit FDA Prior Notice (8 hours before USA sea arrivals)
- File export declaration with customs
- Obtain port clearance and loading permits
- Verify all certificates are current
Post-Shipment (24-48 Hours After)
- Obtain signed Bill of Lading from carrier
- Send documents to buyer or bank
- File copies for regulatory retention
- Update tracking systems
Understanding the growing demand for Himalayan pink salt helps exporters anticipate documentation requirements for expanding markets and prepare accordingly.
Common Documentation Errors and Solutions
Error #1: Incorrect HS Code Classification
- Problem: Wrong tariff codes lead to duty assessment errors
- Solution: Consult official HS Code databases or customs brokers for accurate classification
Error #2: Inconsistent Product Descriptions
- Problem: Different descriptions across documents raise red flags
- Solution: Use identical product descriptions on all documents from single master template
Error #3: Missing Signatures or Seals
- Problem: Unsigned certificates lack legal validity
- Solution: Create document checklist requiring verification of all signatures before submission
Error #4: Expired Certificates
- Problem: Outdated health or quality certificates cause rejection
- Solution: Track certificate expiration dates and renew proactively before shipments
Error #5: Incomplete Commercial Invoice
- Problem: Missing required elements delay customs clearance
- Solution: Use standardized invoice templates with all mandatory fields
For importers new to how to import Himalayan salt from Pakistan, working with experienced export partners minimizes documentation errors through established procedures and compliance systems.
Digital Documentation Trends
Electronic documentation represents the future of international trade, offering significant advantages over traditional paper systems. The WTO’s Agreement on Trade Facilitation encourages members to accept paper or electronic copies of supporting documents for import, export, and transit formalities.
Key Digital Documentation Benefits:
- Reduced processing time from days to hours for exporters
- Faster customs clearance with lower document loss risks for importers
- Electronic verification systems reduce fraud for customs authorities
- Lower administrative costs across all parties
Many European and Asia-Pacific countries have issued electronic Certificates of Origin for decades, with China extensively utilizing eCOs in daily trade operations [1].
Working with Professional Salt Exporters
Experienced Himalayan salt manufacturers in Pakistan provide comprehensive documentation support. Professional exporters handle Certificate of Origin procurement, commercial invoice preparation, Bill of Lading coordination, health certificate arrangement, FDA Prior Notice submission, and export declaration filing.
For buyers sourcing black salt and specialty products, comprehensive documentation support ensures product authenticity and regulatory compliance across diverse market requirements.
Conclusion
Successful salt export documentation requires understanding core documents, regulatory requirements, preparation timelines, and digital solutions. Certificate of Origin proves product nationality, Bill of Lading provides title and contract functions, and Commercial Invoice enables customs assessment. Health certificates, quality reports, and packing lists complete the documentation framework for compliant international trade.
For B2B salt importers and exporters, proper documentation protects legal interests, facilitates customs clearance, and ensures smooth supply chain operations. Partnering with experienced manufacturers who understand documentation requirements reduces compliance risks and accelerates market entry for global Himalayan salt trade.
References
[1]: International Chamber of Commerce. (2025). Certificates of Origin Guidelines. ICC World Chambers Federation establishes universal procedures for CO issuance followed by millions of annual certificates globally. https://iccwbo.org/business-solutions/certificates-of-origin/
[2]: International Trade Administration. (2024). FTA Certificates of Origin Requirements. U.S. Department of Commerce guidance on certificate requirements for Free Trade Agreement partners. https://www.trade.gov/fta-certificates-origin
[3]: Wikipedia. (2025). Bill of Lading – International Trade Document. Comprehensive overview of B/L functions including receipt, contract, and title document roles in global trade. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bill_of_lading
[4]: U.S. Customs and Border Protection. (2024). Commercial Invoice Requirements – 19 CFR 142.6. Federal regulations requiring eight-digit HS Code and complete product information for customs clearance. https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-19/chapter-I/part-142/subpart-A/section-142.6
[5]: Inbound Logistics. (2025). Commercial Invoice: Definition and Terms. Detailed explanation of commercial invoice role in facilitating customs processing and determining applicable tariffs. https://www.inboundlogistics.com/articles/commercial-invoice/
[6]: iContainers. (2024). What is a Commercial Invoice – Example. Legal document requirements and differences between commercial invoices and packing lists in international freight shipping. https://www.icontainers.com/help/what-is-a-commercial-invoice/
Share This Post
Article By

